Protein-coding gene in humans
| ATP5F1B |
|---|
 |
| Identifiers |
|---|
| Aliases | ATP5F1B, ATPMB, ATPSB, HEL-S-271, ATP synthase, H+ transporting, mitochondrial F1 complex, beta polypeptide, ATP synthase F1 subunit beta, ATP5B |
|---|
| External IDs | OMIM: 102910; MGI: 107801; HomoloGene: 1273; GeneCards: ATP5F1B; OMA:ATP5F1B - orthologs |
|---|
| Gene location (Human) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 12 (human)[1] |
|---|
| | Band | 12q13.3 | Start | 56,638,175 bp[1] |
|---|
| End | 56,645,984 bp[1] |
|---|
|
| Gene location (Mouse) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 10 (mouse)[2] |
|---|
| | Band | 10|10 D3 | Start | 127,919,142 bp[2] |
|---|
| End | 127,926,260 bp[2] |
|---|
|
| RNA expression pattern |
|---|
| Bgee | | Human | Mouse (ortholog) |
|---|
| Top expressed in | - apex of heart
- left ventricle
- right auricle
- right ventricle
- myocardium of left ventricle
- mucosa of transverse colon
- cerebellar cortex
- right hemisphere of cerebellum
- muscle of thigh
- gastrocnemius muscle
|
| | Top expressed in | - right kidney
- dentate gyrus of hippocampal formation granule cell
- myocardium of ventricle
- right ventricle
- atrium
- central gray substance of midbrain
- mandibular prominence
- cardiac muscles
- human kidney
- maxillary prominence
|
| | More reference expression data |
|
|---|
| BioGPS | 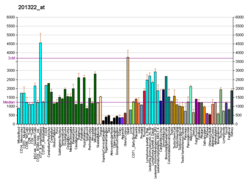
 | | More reference expression data |
|
|---|
|
| Gene ontology |
|---|
| Molecular function | - nucleotide binding
- transmembrane transporter activity
- transporter activity
- proton-transporting ATPase activity, rotational mechanism
- ATPase activity
- protein binding
- MHC class I protein binding
- hydrolase activity
- ATP binding
- angiostatin binding
- proton-transporting ATP synthase activity, rotational mechanism
| | Cellular component | - mitochondrial proton-transporting ATP synthase complex
- membrane
- mitochondrial membranes
- myelin sheath
- plasma membrane
- cell surface
- mitochondrial matrix
- mitochondrial proton-transporting ATP synthase, catalytic core
- mitochondrion
- mitochondrial inner membrane
- proton-transporting ATP synthase complex, catalytic core F(1)
- mitochondrial nucleoid
- extracellular exosome
- nucleus
- extracellular matrix
- proton-transporting ATP synthase complex
- proton-transporting two-sector ATPase complex, catalytic domain
| | Biological process | - lipid metabolism
- mitochondrial ATP synthesis coupled proton transport
- mitochondrion organization
- regulation of intracellular pH
- ion transport
- generation of precursor metabolites and energy
- negative regulation of cell adhesion involved in substrate-bound cell migration
- ATP metabolic process
- angiogenesis
- osteoblast differentiation
- ATP synthesis coupled proton transport
- ATP biosynthetic process
- cristae formation
- positive regulation of blood vessel endothelial cell migration
- transport
- cellular response to interleukin-7
- proton transmembrane transport
| | Sources:Amigo / QuickGO |
|
| Orthologs |
|---|
| Species | Human | Mouse |
|---|
| Entrez | | |
|---|
| Ensembl | | |
|---|
| UniProt | | |
|---|
| RefSeq (mRNA) | | |
|---|
| RefSeq (protein) | | |
|---|
| Location (UCSC) | Chr 12: 56.64 – 56.65 Mb | Chr 10: 127.92 – 127.93 Mb |
|---|
| PubMed search | [3] | [4] |
|---|
|
| Wikidata |
| View/Edit Human | View/Edit Mouse |
|
ATP synthase F1 subunit beta, mitochondrial is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ATP5F1B gene.[5][6]
Function
This gene encodes a subunit of mitochondrial ATP synthase. Mitochondrial ATP synthase catalyzes ATP synthesis, utilizing an electrochemical gradient of protons across the inner membrane during oxidative phosphorylation. ATP synthase is composed of two linked multi-subunit complexes: the soluble catalytic core, F1, and the membrane-spanning component, Fo, comprising the proton channel. The catalytic portion of mitochondrial ATP synthase consists of 5 different subunits (alpha, beta, gamma, delta, and epsilon) assembled with a stoichiometry of 3 alpha, 3 beta, and a single representative of the other 3. The proton channel consists of three main subunits (a, b, c). This gene encodes the beta subunit of the catalytic core.[6]
References
- ^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000110955 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000025393 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ Neckelmann N, Warner CK, Chung A, Kudoh J, Minoshima S, Fukuyama R, Maekawa M, Shimizu Y, Shimizu N, Liu JD (Jan 1990). "The human ATP synthase beta subunit gene: sequence analysis, chromosome assignment, and differential expression". Genomics. 5 (4): 829–43. doi:10.1016/0888-7543(89)90125-0. PMID 2687158.
- ^ a b "Entrez Gene: ATP5F1B ATP synthase F1 subunit beta".
External links
Further reading
- Maguire D, Shah J, McCabe M (2007). "Assaying ATP Synthase Rotor Activity". Oxygen Transport to Tissue XXVII. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology. Vol. 578. pp. 67–72. doi:10.1007/0-387-29540-2_11. ISBN 978-0-387-29543-5. PMID 16927672.
- Dawson SJ, White LA (1992). "Treatment of Haemophilus aphrophilus endocarditis with ciprofloxacin". J. Infect. 24 (3): 317–20. doi:10.1016/S0163-4453(05)80037-4. PMID 1602151.
- Ohta S, Kagawa Y (1986). "Human F1-ATPase: molecular cloning of cDNA for the beta subunit". J. Biochem. 99 (1): 135–41. doi:10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135452. PMID 2870059.
- Wallace DC, Ye JH, Neckelmann SN, Singh G, Webster KA, Greenberg BD (1988). "Sequence analysis of cDNAs for the human and bovine ATP synthase beta subunit: mitochondrial DNA genes sustain seventeen times more mutations". Curr. Genet. 12 (2): 81–90. doi:10.1007/BF00434661. PMID 2896550. S2CID 20431715.
- Ohta S, Tomura H, Matsuda K, Kagawa Y (1988). "Gene structure of the human mitochondrial adenosine triphosphate synthase beta subunit". J. Biol. Chem. 263 (23): 11257–62. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(18)37950-X. PMID 2900241.
- Villena JA, Martin I, Viñas O, Cormand B, Iglesias R, Mampel T, Giralt M, Villarroya F (1995). "ETS transcription factors regulate the expression of the gene for the human mitochondrial ATP synthase beta-subunit". J. Biol. Chem. 269 (51): 32649–54. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(18)31683-1. PMID 7798271.
- Abrahams JP, Leslie AG, Lutter R, Walker JE (1994). "Structure at 2.8 A resolution of F1-ATPase from bovine heart mitochondria". Nature. 370 (6491): 621–8. Bibcode:1994Natur.370..621A. doi:10.1038/370621a0. PMID 8065448. S2CID 4275221.
- Elston T, Wang H, Oster G (1998). "Energy transduction in ATP synthase". Nature. 391 (6666): 510–3. Bibcode:1998Natur.391..510E. doi:10.1038/35185. PMID 9461222. S2CID 4406161.
- Wang H, Oster G (1998). "Energy transduction in the F1 motor of ATP synthase". Nature. 396 (6708): 279–82. Bibcode:1998Natur.396..279W. doi:10.1038/24409. PMID 9834036. S2CID 4424498.
- Moser TL, Stack MS, Asplin I, Enghild JJ, Højrup P, Everitt L, Hubchak S, Schnaper HW, Pizzo SV (1999). "Angiostatin binds ATP synthase on the surface of human endothelial cells". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 96 (6): 2811–6. Bibcode:1999PNAS...96.2811M. doi:10.1073/pnas.96.6.2811. PMC 15851. PMID 10077593.
- Wang ZG, White PS, Ackerman SH (2001). "Atp11p and Atp12p are assembly factors for the F(1)-ATPase in human mitochondria". J. Biol. Chem. 276 (33): 30773–8. doi:10.1074/jbc.M104133200. PMID 11410595.
- Andersen JS, Lyon CE, Fox AH, Leung AK, Lam YW, Steen H, Mann M, Lamond AI (2002). "Directed proteomic analysis of the human nucleolus". Curr. Biol. 12 (1): 1–11. doi:10.1016/S0960-9822(01)00650-9. PMID 11790298. S2CID 14132033.
- Ackerman SH (2002). "Atp11p and Atp12p are chaperones for F(1)-ATPase biogenesis in mitochondria". Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1555 (1–3): 101–5. doi:10.1016/S0005-2728(02)00262-1. PMID 12206899.
- Martinez LO, Jacquet S, Esteve JP, Rolland C, Cabezón E, Champagne E, Pineau T, Georgeaud V, Walker JE, Tercé F, Collet X, Perret B, Barbaras R (2003). "Ectopic beta-chain of ATP synthase is an apolipoprotein A-I receptor in hepatic HDL endocytosis". Nature. 421 (6918): 75–9. Bibcode:2003Natur.421...75M. doi:10.1038/nature01250. PMID 12511957. S2CID 4333137.
- Reuter TY, Medhurst AL, Waisfisz Q, Zhi Y, Herterich S, Hoehn H, Gross HJ, Joenje H, Hoatlin ME, Mathew CG, Huber PA (2003). "Yeast two-hybrid screens imply involvement of Fanconi anemia proteins in transcription regulation, cell signaling, oxidative metabolism, and cellular transport". Exp. Cell Res. 289 (2): 211–21. doi:10.1016/S0014-4827(03)00261-1. PMID 14499622.
- Cross RL (2004). "Molecular motors: turning the ATP motor". Nature. 427 (6973): 407–8. Bibcode:2004Natur.427..407C. doi:10.1038/427407b. PMID 14749816. S2CID 52819856.
- Aboulaich N, Vainonen JP, Strålfors P, Vener AV (2005). "Vectorial proteomics reveal targeting, phosphorylation and specific fragmentation of polymerase I and transcript release factor (PTRF) at the surface of caveolae in human adipocytes". Biochem. J. 383 (Pt 2): 237–48. doi:10.1042/BJ20040647. PMC 1134064. PMID 15242332.
- Jin J, Smith FD, Stark C, Wells CD, Fawcett JP, Kulkarni S, Metalnikov P, O'Donnell P, Taylor P, Taylor L, Zougman A, Woodgett JR, Langeberg LK, Scott JD, Pawson T (2004). "Proteomic, functional, and domain-based analysis of in vivo 14-3-3 binding proteins involved in cytoskeletal regulation and cellular organization". Curr. Biol. 14 (16): 1436–50. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2004.07.051. PMID 15324660. S2CID 2371325.
PDB gallery
-
1bmf: BOVINE MITOCHONDRIAL F1-ATPASE -
1cow: BOVINE MITOCHONDRIAL F1-ATPASE COMPLEXED WITH AUROVERTIN B -
1e1q: BOVINE MITOCHONDRIAL F1-ATPASE AT 100K -
1e1r: BOVINE MITOCHONDRIAL F1-ATPASE INHIBITED BY MG2+ADP AND ALUMINIUM FLUORIDE -
1e79: BOVINE F1-ATPASE INHIBITED BY DCCD (DICYCLOHEXYLCARBODIIMIDE) -
1efr: BOVINE MITOCHONDRIAL F1-ATPASE COMPLEXED WITH THE PEPTIDE ANTIBIOTIC EFRAPEPTIN -
1h8e: (ADP.ALF4)2(ADP.SO4) BOVINE F1-ATPASE (ALL THREE CATALYTIC SITES OCCUPIED) -
1h8h: BOVINE MITOCHONDRIAL F1-ATPASE CRYSTALLISED IN THE PRESENCE OF 5MM AMPPNP -
1mab: RAT LIVER F1-ATPASE -
1nbm: THE STRUCTURE OF BOVINE F1-ATPASE COVALENTLY INHIBITED WITH 4-CHLORO-7-NITROBENZOFURAZAN -
1ohh: BOVINE MITOCHONDRIAL F1-ATPASE COMPLEXED WITH THE INHIBITOR PROTEIN IF1 -
1w0j: BERYLLIUM FLUORIDE INHIBITED BOVINE F1-ATPASE -
1w0k: BERYLLIUM FLUORIDE INHIBITED BOVINE F1-ATPASE -
2ck3: AZIDE INHIBITED BOVINE F1-ATPASE -
2f43: Rat liver F1-ATPase -
2jdi: GROUND STATE STRUCTURE OF F1-ATPASE FROM BOVINE HEART MITOCHONDRIA (BOVINE F1-ATPASE CRYSTALLISED IN THE ABSENCE OF AZIDE) |
 | This article on a gene on human chromosome 12 is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |

 1bmf: BOVINE MITOCHONDRIAL F1-ATPASE
1bmf: BOVINE MITOCHONDRIAL F1-ATPASE 1cow: BOVINE MITOCHONDRIAL F1-ATPASE COMPLEXED WITH AUROVERTIN B
1cow: BOVINE MITOCHONDRIAL F1-ATPASE COMPLEXED WITH AUROVERTIN B 1e1q: BOVINE MITOCHONDRIAL F1-ATPASE AT 100K
1e1q: BOVINE MITOCHONDRIAL F1-ATPASE AT 100K 1e1r: BOVINE MITOCHONDRIAL F1-ATPASE INHIBITED BY MG2+ADP AND ALUMINIUM FLUORIDE
1e1r: BOVINE MITOCHONDRIAL F1-ATPASE INHIBITED BY MG2+ADP AND ALUMINIUM FLUORIDE 1e79: BOVINE F1-ATPASE INHIBITED BY DCCD (DICYCLOHEXYLCARBODIIMIDE)
1e79: BOVINE F1-ATPASE INHIBITED BY DCCD (DICYCLOHEXYLCARBODIIMIDE) 1efr: BOVINE MITOCHONDRIAL F1-ATPASE COMPLEXED WITH THE PEPTIDE ANTIBIOTIC EFRAPEPTIN
1efr: BOVINE MITOCHONDRIAL F1-ATPASE COMPLEXED WITH THE PEPTIDE ANTIBIOTIC EFRAPEPTIN 1h8e: (ADP.ALF4)2(ADP.SO4) BOVINE F1-ATPASE (ALL THREE CATALYTIC SITES OCCUPIED)
1h8e: (ADP.ALF4)2(ADP.SO4) BOVINE F1-ATPASE (ALL THREE CATALYTIC SITES OCCUPIED) 1h8h: BOVINE MITOCHONDRIAL F1-ATPASE CRYSTALLISED IN THE PRESENCE OF 5MM AMPPNP
1h8h: BOVINE MITOCHONDRIAL F1-ATPASE CRYSTALLISED IN THE PRESENCE OF 5MM AMPPNP 1mab: RAT LIVER F1-ATPASE
1mab: RAT LIVER F1-ATPASE 1nbm: THE STRUCTURE OF BOVINE F1-ATPASE COVALENTLY INHIBITED WITH 4-CHLORO-7-NITROBENZOFURAZAN
1nbm: THE STRUCTURE OF BOVINE F1-ATPASE COVALENTLY INHIBITED WITH 4-CHLORO-7-NITROBENZOFURAZAN 1ohh: BOVINE MITOCHONDRIAL F1-ATPASE COMPLEXED WITH THE INHIBITOR PROTEIN IF1
1ohh: BOVINE MITOCHONDRIAL F1-ATPASE COMPLEXED WITH THE INHIBITOR PROTEIN IF1 1w0j: BERYLLIUM FLUORIDE INHIBITED BOVINE F1-ATPASE
1w0j: BERYLLIUM FLUORIDE INHIBITED BOVINE F1-ATPASE 1w0k: BERYLLIUM FLUORIDE INHIBITED BOVINE F1-ATPASE
1w0k: BERYLLIUM FLUORIDE INHIBITED BOVINE F1-ATPASE 2ck3: AZIDE INHIBITED BOVINE F1-ATPASE
2ck3: AZIDE INHIBITED BOVINE F1-ATPASE 2f43: Rat liver F1-ATPase
2f43: Rat liver F1-ATPase 2jdi: GROUND STATE STRUCTURE OF F1-ATPASE FROM BOVINE HEART MITOCHONDRIA (BOVINE F1-ATPASE CRYSTALLISED IN THE ABSENCE OF AZIDE)
2jdi: GROUND STATE STRUCTURE OF F1-ATPASE FROM BOVINE HEART MITOCHONDRIA (BOVINE F1-ATPASE CRYSTALLISED IN THE ABSENCE OF AZIDE)




































