Esophageal plexus
| Esophageal plexus | |
|---|---|
 The tracheobronchial lymph glands. (Esophageal plexus visible at bottom center.) | |
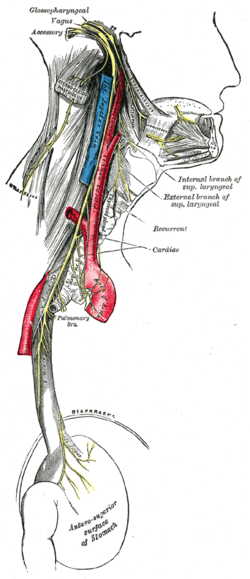 Course and distribution of the glossopharyngeal, vagus, and accessory nerves. | |
| Details | |
| From | Vagus nerve and sympathetic trunk |
| To | Esophagus (same fibers make up the cardiac plexus) |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | plexus oesophageus |
| TA98 | A14.2.01.173 A14.3.03.015 |
| TA2 | 6690 |
| FMA | 6225 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy [edit on Wikidata] | |
The esophageal plexus (oesophageal plexus in British-English) is formed by nerve fibers from two sources, branches of the vagus nerve,[1][2] and visceral branches of the sympathetic trunk.[3][4] The esophageal plexus and the cardiac plexus contain the same types of fibers and are both considered thoracic autonomic plexus.
Parasympathetic fibers
The vagus nerve delivers two fiber types to the esophageal plexus:
- Parasympathetic preganglionic fibers - These fibers have their cell bodies located in the dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus and they will synapse on the terminal ganglia in the walls of the esophagus.
- Afferent fibers - These fibers are primarily concerned with autonomic reflexes and they have their cell bodies in the inferior ganglion of the vagus.
These vagal fibers in the esophageal plexus reform to make the anterior vagal trunk (left vagus) and the posterior vagal trunk (right vagus).[1] Anterior and posterior being terms in relation to the esophagus, a mnemonic for which is 'LARP': Left becomes Anterior, Right becomes Posterior.
Sympathetic fibers
The visceral branches of the sympathetic trunk also deliver two fiber types to the esophageal plexus:
- Sympathetic postganglionic fibers - The cell bodies of these fibers are located in the sympathetic chain ganglia . The cell bodies of the preganglionic fibers, the first neuron of this two neuron chain, are located in the intermediolateral cell column (IMLCC) of the thoracic spinal cord.
- Afferent fibers - These fibers are primarily concerned with pain and have cell bodies located in the dorsal root ganglion.
Additional images
-
 The right sympathetic chain and its connections with the thoracic, abdominal, and pelvic plexuses.
The right sympathetic chain and its connections with the thoracic, abdominal, and pelvic plexuses.
See also
- Esophagus
- Cardiac plexus
- Thoracic autonomic plexus
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 913 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 913 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- ^ a b Rea, Paul (2014-01-01), Rea, Paul (ed.), "Chapter 10 - Vagus Nerve", Clinical Anatomy of the Cranial Nerves, San Diego: Academic Press, pp. 105–116, doi:10.1016/b978-0-12-800898-0.00010-5, ISBN 978-0-12-800898-0, retrieved 2020-11-20
- ^ Benarroch, E. E. (2014-01-01), "Vagus Nerve (Cranial Nerve X)", in Aminoff, Michael J.; Daroff, Robert B. (eds.), Encyclopedia of the Neurological Sciences (Second Edition), Oxford: Academic Press, pp. 589–590, doi:10.1016/b978-0-12-385157-4.00516-9, ISBN 978-0-12-385158-1, retrieved 2020-11-20
- ^ Longbottom, Jennie (2010-01-01), Longbottom, Jennie (ed.), "6 - The thoracic spine", Acupuncture in Manual Therapy, Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone, pp. 93–112, doi:10.1016/b978-0-443-06782-2.00006-2, ISBN 978-0-443-06782-2, retrieved 2020-11-20
- ^ Gardner, ERNEST D.; Bunge, RICHARD P. (2005-01-01), Dyck, Peter J.; Thomas, P. K. (eds.), "Chapter 2 - Gross Anatomy of the Peripheral Nervous System", Peripheral Neuropathy (Fourth Edition), Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders, pp. 11–33, doi:10.1016/b978-0-7216-9491-7.50005-3, ISBN 978-0-7216-9491-7, retrieved 2020-11-20
External links
- Anatomy photo:21:11-0105 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "Mediastinum: The Esophageal Plexus"
- v
- t
- e
| Sympathetic | |
|---|---|
| Parasympathetic |
| Sympathetic |
|---|
| Sympathetic |
|
|---|
| Sympathetic | |
|---|---|
| Enteric |
| Sympathetic | |
|---|---|
| Parasympathetic |
 Category
Category Commons
Commons















