Polidocanol
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names |
|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | topical, subcutaneous injection |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID |
|
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII |
|
| KEGG |
|
| ChEMBL |
|
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.019.351 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C30H62O10 |
| Molar mass | 582.816 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) |
|
| |
| |
 N N Y (what is this?) (verify) Y (what is this?) (verify) | |
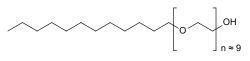
Polidocanol is a local anaesthetic and antipruritic component of ointments and bath additives. It relieves itching caused by eczema and dry skin.[2] It has also been used to treat varicose veins,[3] hemangiomas, and vascular malformations.[4] It is formed by the ethoxylation of dodecanol.
Sclerotherapy
Polidocanol is also used as a sclerosant, an irritant injected to treat varicose veins, under the trade names Asclera, Aethoxysklerol[5] and Varithena.[6] Polidocanol causes fibrosis inside varicose veins, occluding the lumen of the vessel, and reducing the appearance of the varicosity.
The FDA has approved polidocanol injections for the treatment of small varicose (less than 1 mm in diameter) and reticular veins (1 to 3 mm in diameter). Polidocanol works by damaging the cell lining of blood vessels, causing them to close and eventually be replaced by other types of tissue.[7][8] Polidocanol in the form of Varithena injected in the greater saphenous vein can cause the eruption of varicose and spider veins throughout the lower leg. This procedure should be done with caution and with the knowledge that the appearance of the leg may be forever compromised.

References
- ^ "Health Canada New Drug Authorizations: 2015 Highlights". Health Canada. 4 May 2016. Retrieved 7 April 2024.
- ^ "E45 itch relief cream". netdoctor.co.uk. Retrieved 2007-07-12.
- ^ Star P, Connor DE, Parsi K (April 2018). "Novel developments in foam sclerotherapy: Focus on Varithena (polidocanol endovenous microfoam) in the management of varicose veins". Phlebology. 33 (3): 150–162. doi:10.1177/0268355516687864. PMID 28166694.
- ^ Gao Z, Zhang Y, Li W, Shi C (January 2018). "Effectiveness and safety of polidocanol for the treatment of hemangiomas and vascular malformations: A meta-analysis". Dermatologic Therapy. 31 (1). doi:10.1111/dth.12568. PMID 29082587.
- ^ Sclerotherapy, Laurence Z Rosenberg, MD, eMedicine.com
- ^ "Varithena (polidocanol injectable foam) For Intravenous Use. Full Prescribing Information" (PDF). Biocompatibles, Inc. Archived from the original (PDF) on 4 August 2016. Retrieved 1 October 2015.
- ^ Facts and Companies: Varicose Vein Treatment Approved
- ^ "Asclera Full Prescribing Information in Drug Reference Encyclopedia". Retrieved 2010-04-11.
- v
- t
- e
| corticosteroids | |
|---|---|
| local anesthetics | |
| other |
| heparins or heparinoids for topical use | |
|---|---|
| sclerosing agents for local injection | |
| other |
| bioflavonoids | |
|---|---|
| other |
 | This drug article relating to the cardiovascular system is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
- v
- t
- e
 | This dermatologic drug article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
- v
- t
- e










