| P2RX2 |
|---|
|
| Identifiers |
|---|
| Aliases | P2RX2, DFNA41, P2X2, purinergic receptor P2X 2 |
|---|
| External IDs | OMIM: 600844; MGI: 2665170; HomoloGene: 14251; GeneCards: P2RX2; OMA:P2RX2 - orthologs |
|---|
| Gene location (Human) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 12 (human)[1] |
|---|
| | Band | 12q24.33 | Start | 132,618,776 bp[1] |
|---|
| End | 132,622,388 bp[1] |
|---|
|
| Gene location (Mouse) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 5 (mouse)[2] |
|---|
| | Band | 5|5 F | Start | 110,487,678 bp[2] |
|---|
| End | 110,491,078 bp[2] |
|---|
|
| RNA expression pattern |
|---|
| Bgee | | Human | Mouse (ortholog) |
|---|
| Top expressed in | - gastric mucosa
- right lung
- right uterine tube
- prostate
- caput epididymis
- corpus epididymis
- hippocampus proper
- spleen
- upper lobe of left lung
- amygdala
|
| | Top expressed in | - otolith organ
- utricle
- seminiferous tubule
- spermatocyte
- spermatid
- cochlea
- stria vascularis
- prostate
- Greater petrosal nerve
- neural tube
|
| | More reference expression data |
|
|---|
| BioGPS | 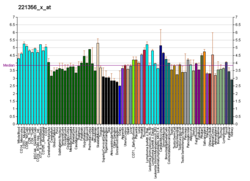
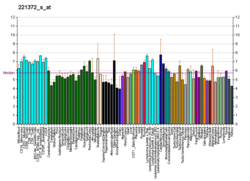 | | More reference expression data |
|
|---|
|
| Gene ontology |
|---|
| Molecular function | - purinergic nucleotide receptor activity
- extracellularly ATP-gated cation channel activity
- ion channel activity
- ligand-gated ion channel activity
- identical protein binding
- ATP binding
- ATP-gated ion channel activity
| | Cellular component | - integral component of membrane
- membrane
- receptor complex
- integral component of nuclear inner membrane
- integral component of plasma membrane
- intracellular anatomical structure
- apical plasma membrane
- plasma membrane
- postsynapse
- neuronal cell body
| | Biological process | - peristalsis
- response to ATP
- positive regulation of calcium-mediated signaling
- response to hypoxia
- positive regulation of calcium ion transport into cytosol
- urinary bladder smooth muscle contraction
- hearing
- ion transport
- response to organic substance
- cation transmembrane transport
- neuromuscular synaptic transmission
- behavioral response to pain
- neuromuscular junction development
- skeletal muscle fiber development
- detection of hypoxic conditions in blood by carotid body chemoreceptor signaling
- protein homooligomerization
- response to carbohydrate
- sensory perception of taste
- chemical synaptic transmission
- blood coagulation
- purinergic nucleotide receptor signaling pathway
- excitatory postsynaptic potential
- response to ischemia
- cation transport
- ion transmembrane transport
| | Sources:Amigo / QuickGO |
|
| Orthologs |
|---|
| Species | Human | Mouse |
|---|
| Entrez | | |
|---|
| Ensembl | | |
|---|
| UniProt | | |
|---|
| RefSeq (mRNA) | NM_001282164
NM_001282165
NM_012226
NM_016318
NM_170682
|
|---|
NM_170683
NM_174872
NM_174873 |
| |
|---|
NM_001164833
NM_001164834
NM_153400
NM_001310700
NM_001310701 |
|
|---|
| RefSeq (protein) | NP_001269093
NP_001269094
NP_036358
NP_057402
NP_733782
|
|---|
NP_733783
NP_777361
NP_777362 |
| |
|---|
NP_001158305
NP_001158306
NP_001297629
NP_001297630
NP_700449 |
|
|---|
| Location (UCSC) | Chr 12: 132.62 – 132.62 Mb | Chr 5: 110.49 – 110.49 Mb |
|---|
| PubMed search | [3] | [4] |
|---|
|
| Wikidata |
| View/Edit Human | View/Edit Mouse |
|


















