| KIF20B |
|---|
|
| Identifiers |
|---|
| Aliases | KIF20B, CT90, KRMP1, MPHOSPH1, MPP-1, MPP1, kinesin family member 20B |
|---|
| External IDs | OMIM: 605498; MGI: 2444576; HomoloGene: 9418; GeneCards: KIF20B; OMA:KIF20B - orthologs |
|---|
| Gene location (Human) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 10 (human)[1] |
|---|
| | Band | 10q23.31 | Start | 89,701,590 bp[1] |
|---|
| End | 89,774,939 bp[1] |
|---|
|
| Gene location (Mouse) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 19 (mouse)[2] |
|---|
| | Band | 19|19 C1 | Start | 34,899,761 bp[2] |
|---|
| End | 34,953,145 bp[2] |
|---|
|
| RNA expression pattern |
|---|
| Bgee | | Human | Mouse (ortholog) |
|---|
| Top expressed in | - testicle
- oocyte
- secondary oocyte
- gonad
- ventricular zone
- Achilles tendon
- ganglionic eminence
- trabecular bone
- bone marrow cells
- skin of thigh
|
| | Top expressed in | - genital tubercle
- tail of embryo
- secondary oocyte
- zygote
- hand
- ventricular zone
- primary oocyte
- spermatocyte
- lumbar spinal ganglion
- morula
|
| | More reference expression data |
|
|---|
| BioGPS | 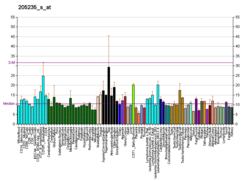 | | More reference expression data |
|
|---|
|
| Gene ontology |
|---|
| Molecular function | - nucleotide binding
- microtubule motor activity
- protein homodimerization activity
- microtubule binding
- ATPase activity
- protein binding
- WW domain binding
- plus-end-directed microtubule motor activity
- ATP binding
| | Cellular component | - cytoplasm
- centrosome
- mitotic spindle pole
- cell projection
- spindle pole
- contractile ring
- kinesin complex
- growth cone
- microtubule cytoskeleton
- spindle
- nucleoplasm
- microtubule organizing center
- mitotic spindle midzone
- axon
- midbody
- nucleolus
- spindle midzone
- perinuclear region of cytoplasm
- microtubule
- cytoskeleton
- nucleus
| | Biological process | - positive regulation of intracellular protein transport
- neuron projection morphogenesis
- cell division
- positive regulation of cytokinesis
- positive regulation of neuron migration
- microtubule-based movement
- positive regulation of mitotic cytokinetic process
- neural tube closure
- protein localization to microtubule
- regulation of establishment of protein localization
- positive regulation of cell population proliferation
- regulation of neuron migration
- cell cycle
- regulation of establishment of cell polarity
- regulation of mitotic nuclear division
| | Sources:Amigo / QuickGO |
|
| Orthologs |
|---|
| Species | Human | Mouse |
|---|
| Entrez | | |
|---|
| Ensembl | | |
|---|
| UniProt | | |
|---|
| RefSeq (mRNA) | |
|---|
NM_016195
NM_001284259
NM_001382506 |
| |
|---|
| RefSeq (protein) | |
|---|
NP_001271188
NP_057279
NP_001369435 |
| |
|---|
| Location (UCSC) | Chr 10: 89.7 – 89.77 Mb | Chr 19: 34.9 – 34.95 Mb |
|---|
| PubMed search | [3] | [4] |
|---|
|
| Wikidata |
| View/Edit Human | View/Edit Mouse |
|


















