| CD300A |
|---|
 |
| Available structures |
|---|
| PDB | Ortholog search: PDBe RCSB |
|---|
|
|
| Identifiers |
|---|
| Aliases | CD300A, CLM-8, CMRF-35-H9, CMRF-35H, CMRF35-H, CMRF35-H9, CMRF35H, CMRF35H9, IGSF12, IRC1, IRC1/IRC2, IRC2, IRp60, CD300a molecule |
|---|
| External IDs | OMIM: 606790; MGI: 2443411; HomoloGene: 48514; GeneCards: CD300A; OMA:CD300A - orthologs |
|---|
| Gene location (Human) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 17 (human)[1] |
|---|
| | Band | 17q25.1 | Start | 74,466,399 bp[1] |
|---|
| End | 74,484,794 bp[1] |
|---|
|
| RNA expression pattern |
|---|
| Bgee | | Human | Mouse (ortholog) |
|---|
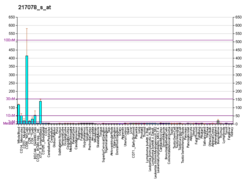
| Top expressed in | - granulocyte
- blood
- monocyte
- spleen
- bone marrow
- bone marrow cells
- amniotic fluid
- appendix
- periodontal fiber
- lymph node
|
| | | More reference expression data |
|
|---|
| BioGPS | 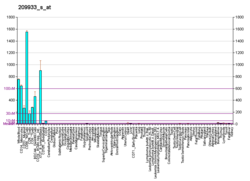
 | | More reference expression data |
|
|---|
|
| Gene ontology |
|---|
| Molecular function | - signaling receptor activity
- phosphatidylethanolamine binding
- phosphatidylserine binding
- protein binding
| | Cellular component | - integral component of membrane
- extracellular exosome
- membrane
- plasma membrane
- tertiary granule membrane
- ficolin-1-rich granule membrane
| | Biological process | - regulation of T cell receptor signaling pathway
- immune system process
- negative regulation of eosinophil migration
- positive regulation of phosphoprotein phosphatase activity
- negative regulation of neutrophil activation
- negative regulation of eosinophil activation
- regulation of immune response
- negative regulation of fibroblast proliferation
- negative regulation of MAP kinase activity
- negative regulation of mast cell degranulation
- negative regulation of mast cell activation involved in immune response
- cell adhesion
- negative regulation of NK T cell activation
- negative regulation of B cell receptor signaling pathway
- negative regulation of activation of Janus kinase activity
- negative regulation of phagocytosis, engulfment
- negative regulation of B cell proliferation
- signal transduction
- negative regulation of MyD88-dependent toll-like receptor signaling pathway
- neutrophil degranulation
| | Sources:Amigo / QuickGO |
|
| Orthologs |
|---|
| Species | Human | Mouse |
|---|
| Entrez | | |
|---|
| Ensembl | | |
|---|
| UniProt | | |
|---|
| RefSeq (mRNA) | |
|---|
NM_001256841
NM_007261
NM_001330456
NM_001330457 |
| |
|---|
NM_170758
NM_001347654
NM_001359812 |
|
|---|
| RefSeq (protein) | |
|---|
NP_001243770
NP_001317385
NP_001317386
NP_009192 |
| |
|---|
NP_001334583
NP_739564
NP_001346741 |
|
|---|
| Location (UCSC) | Chr 17: 74.47 – 74.48 Mb | n/a |
|---|
| PubMed search | [2] | [3] |
|---|
|
| Wikidata |
| View/Edit Human | View/Edit Mouse |
|


















